Avian influenza: tackling large numbers of outbreaks this winter in the UK
Posted: 17 December, 2021
Nearly two years on, the COVID-19 pandemic is still dominating the news and continues to cause concern for populations across the globe. However, UK poultry and wild bird populations are currently facing their own health threat. We are not the only ones that have faced lockdowns because of spreading viruses, UK poultry and captive birds have also faced a similar situation to protect them from avian influenza.
We spoke to Dr Holly Shelton, head of Pirbright’s Influenza Viruses group. Holly’s research group is specifically interested in understanding how genetic changes in influenza A viruses can impact disease spread, host responses to infection and the pathology associated with the disease.
What is avian influenza virus?
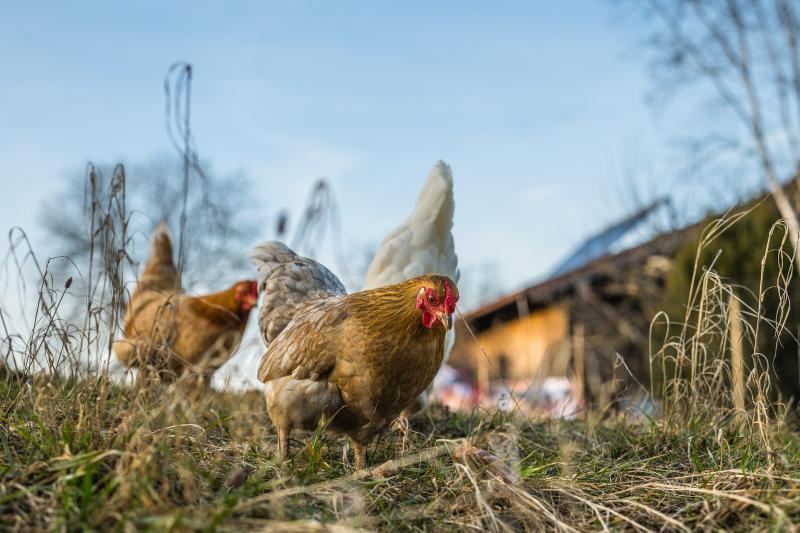
Avian influenza viruses are Influenza A viruses that circulate and transmit amongst birds. The disease is what we commonly know as ‘bird flu’. Influenza A viruses can infect a range of hosts, including humans and two subtypes H1N1 and H3N2 circulate as seasonal flu each winter in the UK. Avian influenza viruses are different to those that can infect humans in that they cannot easily infect humans and must change and adapt to do so.
Aquatic birds are a natural reservoir for avian influenza viruses, these birds typically experience fewer clinical symptoms but can spread disease to domestic birds, particularly in the migratory season, between October and March. Avian influenza viruses are categorised as either highly pathogenic (HPAI) or low pathogenic (LPAI) and this categorisation is linked to the severity of disease in chickens.
HPAI has a high mortality rate which can be up to 100%, other symptoms can include swelling of the head, death of cells in the comb and wattle, red discolouration of legs and feet and diarrhoea. HPAI causes disease in more organs than just those in the respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts like LPAI, which mostly presents as respiratory symptoms such as a snick (like a sneeze), a rattle in the chest (known as rales) and discharge from the eyes and nose.
What is causing bird flu outbreaks in domestic birds now?
We are currently in the normal migratory season of wild birds. In the spring and summer months these birds spend their time breeding and raising their young in North-eastern Asia where they mix with other bird species which enables virus transmission and mutation. Then, when they migrate for the autumn and winter months, they shed virus in their faeces along the way.
One of the migratory paths is across Northern Europe and this includes the UK. This year, in the UK, the first avian influenza outbreak was on 15 October and was discovered in captive aquatic birds. To date (17 December 2021) there have been 50 outbreaks in England, 1 in Wales and 2 in Scotland, this has resulted in over half a million birds being destroyed to control the spread of disease.
Are there more outbreaks this year compared to other years?
The number of outbreaks this year has been the most extensive ever. There have been over 50 outbreaks in the UK, compared to 26 outbreaks last year. Although it is hard to pin down the reason for this high number, we know it is not linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. The UK’s response to the spread of avian influenza has been rapid, and from 29 November birds were required to be housed inside with additional biosecurity measures put in place such as foot dips and disinfecting clothing.
Testing and surveillance of wild birds has shown that there is a high prevalence of the virus in these birds currently, and this is contributing to the spread of disease to farm and domestic bird populations.
A more detailed look at the genetic make-up of these viruses shows that they are different to those from previous years. This is predicted to be as a result of the virus infecting multiple birds across a range of species, and this provides the perfect opportunity for the virus to evolve. Analysis of these genetic changes does not raise any alarm bells for increased transmission to humans, but they are likely impacting the spread and severity of disease in birds.
What should we do if we find a dead bird or are concerned about bird health?
If the public find dead waterfowl birds they are encouraged not to touch them but to report them to Defra using the appropriate phone number that can be found on the website, also any other wild birds found dead in numbers of five or greater should be reported.
What is Pirbright doing to tackle this virus?
Researchers at Pirbright are attempting to enhance control and detection of avian influenza in poultry populations as well as extend our basic knowledge about the virus in avian and mammalian hosts. The Influenza Viruses group lead by Dr Holly Shelton is involved in the assessment of which avian influenza virus strains can rapidly adapt to cause potential infections of humans. In addition, Dr Shelton’s group is mapping the changes in the chicken respiratory and gastrointestinal microbiome (all the microbes that live in the respiratory tract or gut) following influenza virus infection and assessing whether the application of probiotics (‘good bacteria’) can be useful in control virus shedding or transmission in birds. The Avian Influenza group lead by Professor Munir Iqbal is developing improved poultry vaccines that prevent virus replication and spread. These vaccines are particularly useful in countries where avian influenza is regularly found in the domestic poultry and the control and prevention of spread isn’t easy, such as in the UK.
If poultry keepers are concerned more information is available from the Animal and Plant Health Agency (APHA).