Rabies Control: A Model for One Health Collaboration
Rabies and One Health
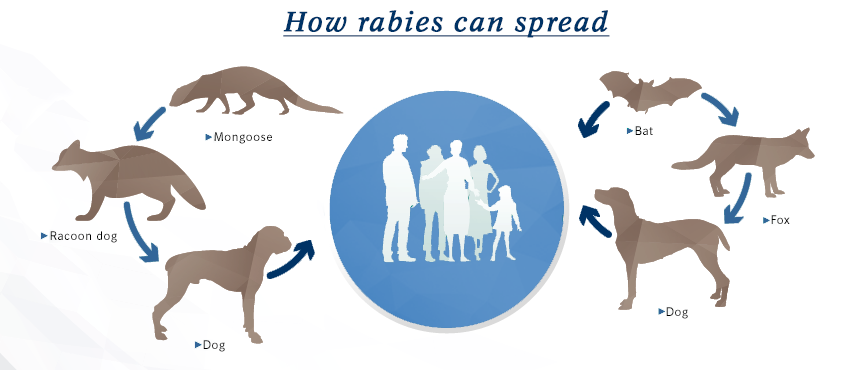
Rabies is a serious disease that can affect both humans and animals. It is important to be aware of the risks of rabies and to take precautions to protect yourself and your family. Rabies is a virus that attacks the nervous system. It usually spreads through an infected animal’s bite, but it can also be spread through contact with saliva or other body fluids from an infected animal. Rabies is fatal if not treated promptly. There are several ways to prevent rabies. One is to avoid contact with wild animals or stray dogs and cats. If you must handle an animal, wear gloves and wash your hands afterwards. Another way to prevent rabies is to vaccinate your pets and make sure they are up-to-date on their vaccinations.
The best way to control rabies is by vaccinating both humans and animals.
There are ways to prevent this deadly disease that could be fatal for both humans and animals. The best way to control rabies is through vaccination of both humans and animals. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the spread of rabies. It is important for people who work with animals, such as veterinarians, to be vaccinated against rabies. People who are exposed to rabies can receive a series of vaccinations to prevent the disease. The first vaccine is given soon after exposure, and additional doses are given over the following weeks. These vaccines are very effective at preventing the disease. Animals can also be vaccinated against rabies. In the United States, laws require that dogs be vaccinated against rabies. Cats, ferrets, and other animals that come in contact with people should also be vaccinated. Vaccinating animals helps to protect both them and us from this serious disease.
The role of veterinarians in rabies control
Rabies is a serious public health concern, and veterinarians play an important role in its control. Rabies is a zoonotic disease, which means it can be transmitted from animals to humans. It is most commonly transmitted through the bite of an infected animal but can also be contracted through contact with saliva or other body fluids. Veterinarians play a key role in rabies control by vaccinating pets and other animals. They also work with public health officials to monitor rabies activity and help educate the public about how to avoid exposure to the virus. In some cases, they may also be called upon to assist with the investigation of suspected rabies cases and the humane euthanasia of rabid animals. The bottom line is that veterinarians are an important part of the team working to keep our communities safe from rabies.
The importance of a cross-sectoral collaboration approach to rabies
The One Health approach to rabies control emphasizes the importance of collaboration between sectors in order to most effectively address the disease. This includes working with human health, animal health, and environmental health practitioners to control the spread of rabies. A cross-sectoral collaboration approach is important because it allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and how it affects different populations. It also allows for the development of more effective control measures that take into account the different needs of each sector.
The benefits of a One Health approach to rabies control
A One Health approach to rabies control is an important step in protecting public health. This approach integrates the efforts of human and animal healthcare workers to control the spread of the disease. A One Health approach is vital because rabies is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. Rabies is a serious disease that can be fatal if not treated promptly. When an animal is infected with rabies, the virus travels to the brain and spinal cord where it causes inflammation and swelling. This can lead to paralysis, seizures, and death. Humans can contract rabies if they are bitten or scratched by an infected animal. A One Health approach to rabies control includes vaccinating dogs and other animals that are at risk for contracting the disease.
Challenges to implementing a One Health approach to rabies control
One Health is an approach to health care that recognizes the interconnectedness of humans, animals, and the environment. Its goal is to promote optimal health for all three by working collaboratively across disciplines. While One Health has great potential for rabies control, there are several challenges to its implementation. One challenge is simply getting people on board with the idea. Because it requires collaboration between so many different sectors, One Health can be difficult to coordinate and implement. There is also a lack of awareness of the approach, which can make it difficult to get buy-in from key stakeholders. Another challenge is that One Health requires a long-term commitment. Rabies control is not something that can be achieved overnight; it requires sustained effort and dedication from everyone involved. This can be difficult to maintain over time, especially when there are other pressing health concerns competing for attention and resources.
Conclusion: the way forward for rabies control
Rabies awareness in different country needs to be increased, Rabies is a preventable disease that affects both humans and animals. In order to control rabies, One Health collaboration is key. This means working together across sectors to address the issue of rabies. The way forward for rabies control is to continue this collaboration and to raise awareness about the importance of preventing rabies. By working together, we can make progress in controlling this disease.
28th of September is the World Rabies Day to increase awarness over the diseas.